What is HIPAA?
HIPAA - Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act - is a law enacted by the U.S. government in 1996 that regulates how healthcare and insurance providers should enable the security and privacy of Protected Health Information (PHI). There have been several amendments and additions to HIPAA, including the HITECH Act in 2009 that strengthened privacy and security provisions, and the 2013 omnibus amendments that expanded HIPAA scope to include subcontractors, and further restricted use of PHI.
HIPAA and the Cloud
HIPAA is comprised of 45 CFR Parts 160 (General Administrative Requirements), 162 (Administrative Requirements), and 164 (Security and Privacy). Part 164 Subpart C details security and privacy standards and notification requirements for HIPAA “covered entities” and their “business associates” that utilize public cloud services to process and store electronic PHI. Relevant citations include:
-
§ 164.306 (Security Standards) - Entities are to protect against any reasonably anticipated threats or hazards to the security or integrity of electronic PHI. Closing sensitive ports on virtual firewalls accessible to the public can prevent bad actors from accessing PHI. VPC and Virtual Network Security Group rules specify ingress/egress to/from ports, and should be configured to avoid potential security gaps.
-
§ 164.308(a)(3) (Administrative Safeguards - Workforce Security) - Entities are to implement procedures for the authorization and/or supervision of workforce members who work with electronic PHI. Specifying strong IAM or Active Directory password policies and rotating credentials help to ensure that PHI is not accessed by bad actors or by unauthorized individuals.
-
§ 164.312(e)(1) (Technical Safeguards - Transmission Security) - Entities are to implement mechanisms to encrypt and decrypt electronic PHI. Resources such as AWS S3 buckets and RDS databases or Azure storage Blobs and SQL databases have configuration options for enabling encryption at-rest and in-transit.
Detect Compliance Violations
Fugue continuously evaluates your cloud environments for HIPAA compliance violations with predefined rules mapped to HIPAA compliance controls. If a resource is determined as non-compliant, an alert will be sent to notify the compliance team. The compliance team can then determine whether to correct the non-compliant resource and set an established baseline for future enforcement.
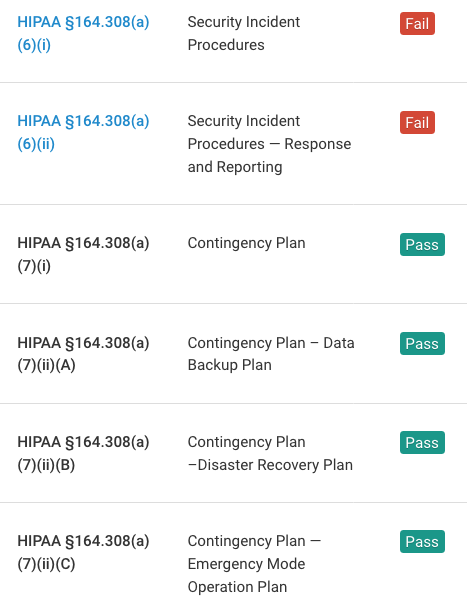
Detect Compliance Violations
Enforce Baselines with Codeless Auto-Remediation
Fugue utilizes baselines to auto-remediate and correct compliance violations via self-healing. With baseline enforcement, misconfiguration is automatically corrected back to the HIPAA-compliant baseline without writing automation scripts.
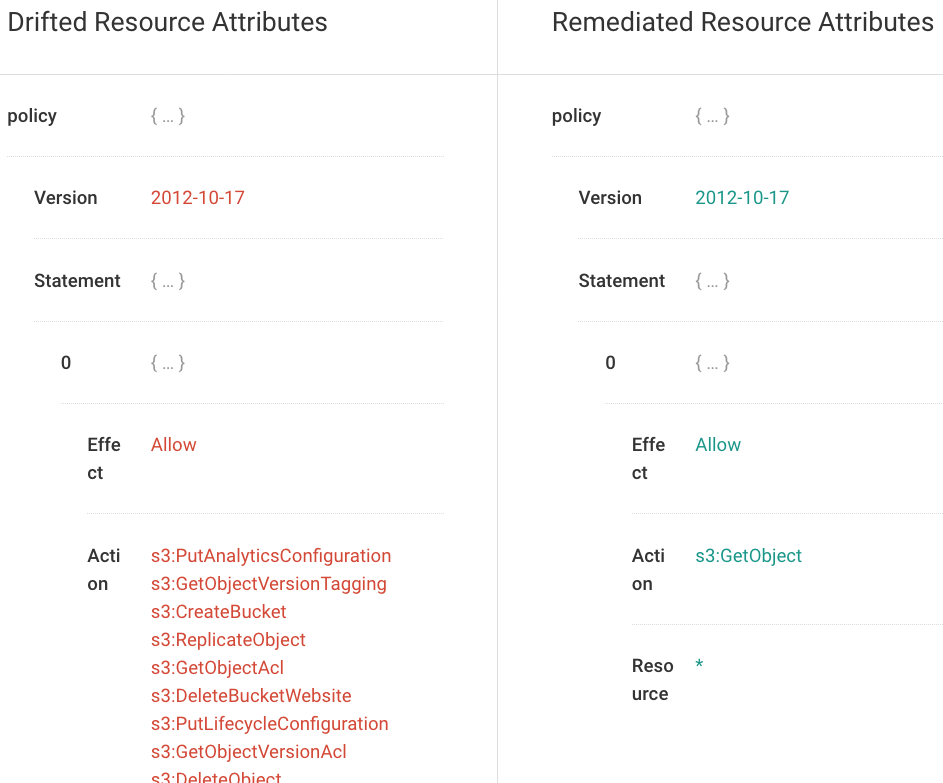
Enforce Baselines with Codeless Auto-Remediation
Report on Compliance Posture
Fugue makes it easy to report on your HIPAA compliance posture. Detailed reports, dashboards, and visualizations are available to easily track and monitor your cloud resources. Daily or weekly reports highlighting compliant and non-compliant resources can be emailed to executives or
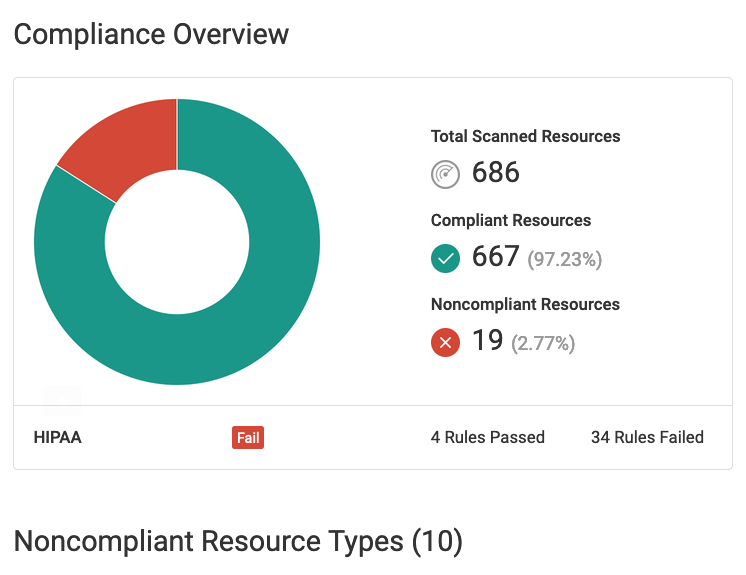
Compliance Overview
